Domain Layer
The Domain Layer encapsulates the logic required to access, manipulate, and commit data. Its primary function is to enforce data integrity, ensuring that your domain entities are always in a valid state.
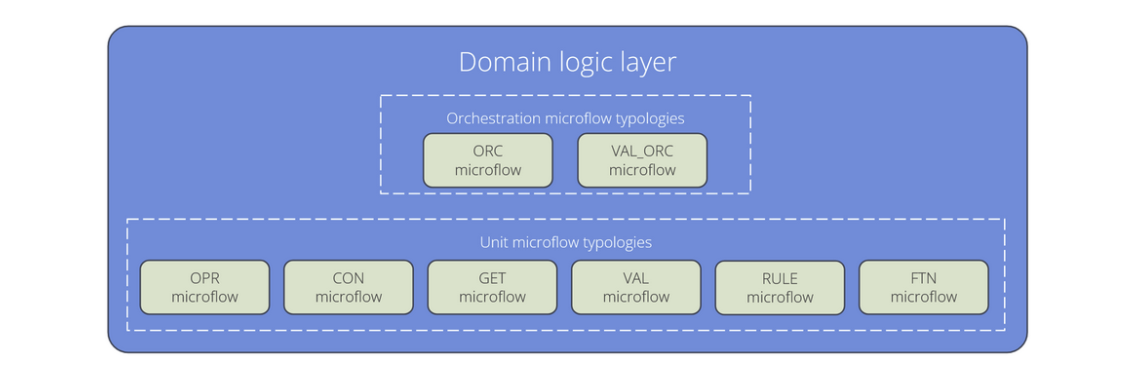
1. Microflow typologies in this layer
This layer is primarily comprised of Unit microflows that are focused on a single responsibility related to your domain entities. The most common unit typologies you will find here are:
- Object Manipulation (
OPR): These microflows are responsible for creating, updating and deleting objects from the database. Note that the operation ‘delete’ means ‘flagging for delete’, because theCMTmicroflow is executing the real delete action. - Object Retrieval (
GET): These microflows are responsible for retrieving objects from the database or by association. - Validation (
VAL): These microflows contain the business rules that validate a domain entity before it is committed.
While Rule microflows (RULE) and Functions (FTN) can exist in this layer, we recommend placing them in the App Logic layer unless their logic is inherently specific to a single domain entity.
The Domain Logic layer can also contain certain Orchestration microflows (ORC and VAL_ORC) when multiple Unit microflows must be executed together to ensure data consistency.
Suppose there is a business rule stating that the credit card number of an existing credit card is immutable. Validating that the credit card number has not been changed requires a sequence of actions, which is implemented by a validation orchestration microflow (VAL_ORC) in the Domain Layer:
- Retrieve: Call a getter microflow (
GET) to fetch the existing credit card by ID from the database. - Validate: Call a validation microflow (
VAL) to verify that the existing credit card number matches the number of the credit card being validated.
The validation microflow (VAL) can be made private, as it should never be called without first performing the retrieve step.